
Why Is Sculpture Made?
Sculpture is made to express emotions ideas and values in a lasting way combining art aesthetics meaning and permanence.
Read Why
Comprehensive Knowledge Guide: We answer all your Why, What is the reason, and How it happens questions with verified facts and accurate information for quick learning. With verified data and real facts, we ensure you get instant access to the precise and clear information you seek, offering reliable answers to all the "why" questions in your mind.
The loss of water or antifreeze in a vehicle's engine cooling system is a critical situation that can lead to engine overheating and severe mechanical damage. Modern internal combustion engines rely on a closed and pressurized cooling system to maintain optimum operating temperature. Fluid loss in this system generally occurs through two main mechanisms: external leakage or mixing into the internal combustion chamber. Correct diagnosis of the water loss problem is vital for the long-lasting and efficient operation of the engine. This academic review aims to analyze in detail why vehicles lose water, the technical reasons behind this situation, and potential failures in cooling system components. The technical reasons behind the water loss of vehicles stem from losses of integrity at various points in the cooling system. These losses accelerate due to the system operating under pressure and usually manifest themselves through visible leaks or evaporation. External Leaks in Cooling System Components The most common failures causing the coolant to leak outward occur in the basic components of the system. These components and their potential failures are as follows: 1. Radiator: Corrosion forming over time in the radiator cores, stone impacts, or vibration-induced cracks cause the fluid to leak out. Especially in radiators with plastic side tanks, leaks are frequently seen at the junction of plastic and metal. 2. Hoses and Connection Points: Rubber components such as radiator hoses, thermostat hoses, and heater hoses harden, crack, or tear due to excessive pressure over time. Loosening at the points where hoses are connected with clamps or the aging of gaskets also leads to leakage. 3. Water Pump: When the shaft seal of the water pump wears out or a crack forms in its body, fluid leakage begins. This leakage, seen in the form of dripping from the discharge hole at the front of the pump, usually indicates that the pump needs to be replaced. 4. Expansion Tank and Cap: Cracks can form in the expansion tank itself. A more critical reason is the failure of the tank cap. The cap is responsible for keeping the pressure in the system at a certain level. When the cap gasket or spring mechanism breaks, the system pressure drops and the boiling point of the water lowers, which causes the fluid to disappear by evaporating. This situation is considered one of the most insidious causes of water loss even though the vehicle does not overheat. Internal Leaks and Structural Damages More serious water loss causes that threaten the integrity of the engine are the mixing of the fluid into the combustion chamber or the lubrication system. 1. Head Gasket Damage: The burning or damage of the gasket between the engine block and the cylinder head creates a transition between the cooling channels and the combustion chamber or oil channels. In this case, the coolant leaks into the combustion chamber and is expelled from the exhaust as white smoke, or it mixes with the engine oil and discolors the oil. This is one of the most critical failures of the engine and requires immediate intervention. 2. Cylinder Head or Engine Block Crack: Thermal stress-induced cracks can form in the cylinder head or engine block as a result of overheating. These cracks also cause water to mix into the combustion chamber or oil, similar to head gasket damage. 3. Heater Core Leakage: Leaks occurring in the heating cores inside the vehicle cause the fluid to leak into the cabin and usually cause a sweet smell and fogging on the windows. The detection of these technical failures is generally carried out with professional diagnostic methods such as pressure testing, chemical tests, and the use of ultraviolet dye. The water loss of vehicles is based on a wide range of technical reasons, from a simple hose looseness to head gasket damage that threatens the structural integrity of the engine. Fundamentally, any leakage point in the closed and pressurized structure of the cooling system or a loss of integrity in the internal structure of the engine leads to water loss. Neglecting this situation causes the engine to overheat and leads to irreversible expensive damages. Therefore, regular maintenance and the immediate inspection of sudden drops in the coolant level by an expert technician is a mandatory precaution for the protection of engine health.

Sculpture is made to express emotions ideas and values in a lasting way combining art aesthetics meaning and permanence.
Read Why
DMD muscular dystrophy results from an X-linked genetic mutation leading to the absence of the dystrophin protein, which is essential for muscle integrity.
Read Why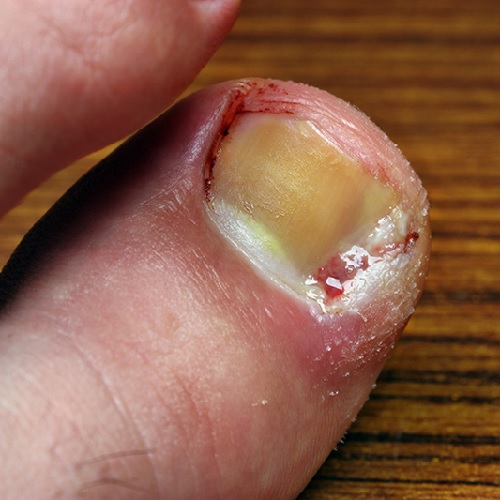
Ingrown toenail is a painful foot problem that occurs due to improper nail trimming, tight shoes and structural nail disorders.
Read Why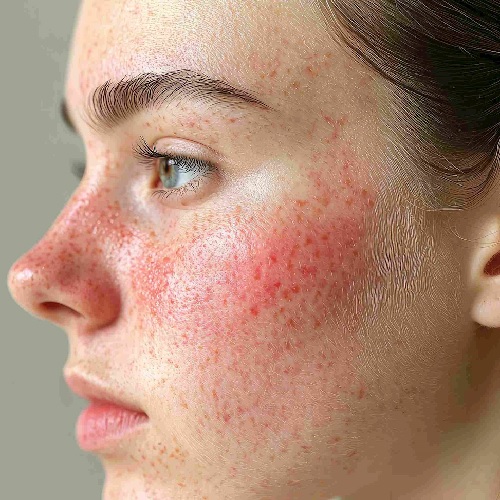
Rosacea is caused by genetic and environmental factors. Sun, stress, and spicy foods trigger redness. Proper care and diagnosis are vital for skin.
Read Why
Brain aneurysm occurs due to weakness in the vessel wall. High blood pressure and smoking increase risks. Early diagnosis is vital for health.
Read Why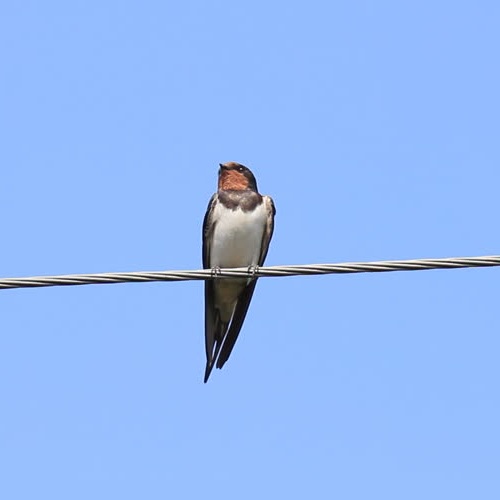
Birds do not get electrocuted on power lines because there is no potential difference and electric current cannot form a closed circuit.
Read Why
Airplane mode reduces energy use by disabling signal search and background connections, allowing the phone battery to last much longer.
Read Why
Facing the Qibla in prayer creates unity focus and discipline The direction of the Kaaba represents devotion obedience and shared belief.
Read Why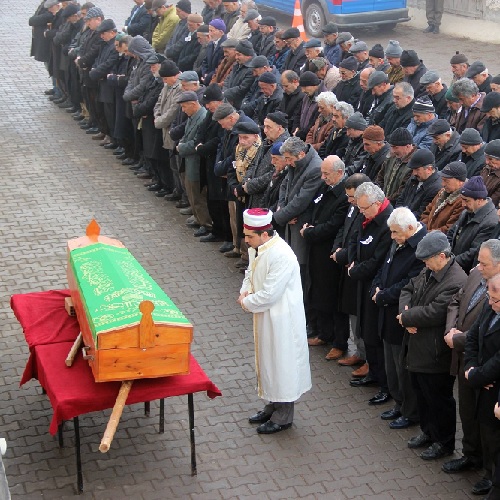
The absence of bowing and prostration in the funeral prayer comes from its prayer focused nature and its purpose as a collective supplication for the deceased.
Read Why
Shifting motorcycle gears with the foot improves safety, balance, ergonomics and control by keeping the rider’s hands on the handlebars.
Read Why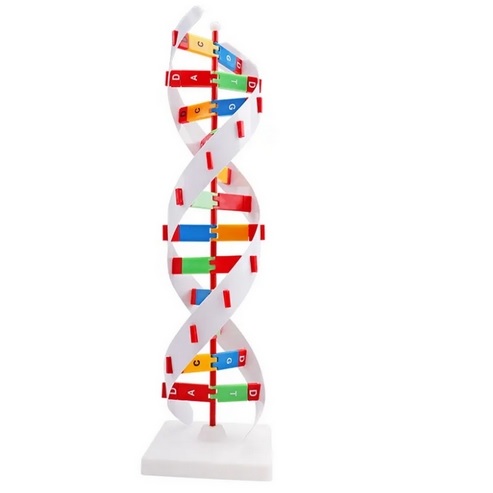
Why Is DNA Double Helix Structure explains how the double helix provides stability accurate replication and reliable protection of genetic information.
Read Why
Why omega 3 supplement is used is related to supporting heart health, brain functions and essential fatty acids balance in the body.
Read Why
The Berlin Wall fell in 1989 due to economic problems and public demand for freedom.
Read Why
The fear of water in rabies occurs because throat muscle spasms prevent the patient from swallowing liquids.
Read Why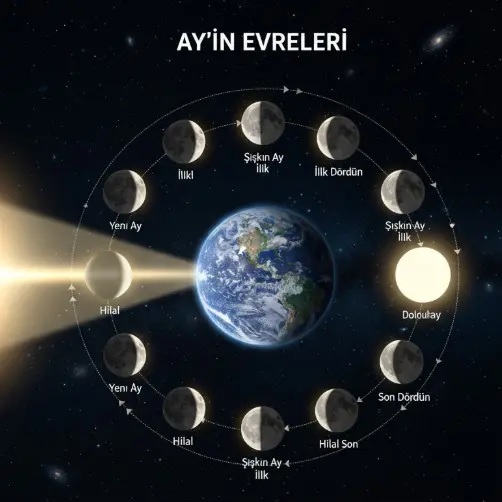
The short answer to why the Moon constantly changes shape is that sunlight reaches it from different angles during its orbit around Earth.
Read Why
The question of why time flows in one direction is explained by physics and entropy because the universe moves toward increasing disorder.
Read Why
Celebrating a holiday observed by Christians with excitement in our country seems to be evidence of being placed in the same category as Christians.
Read Why
Causes of being very sleepy can arise due to fatigue, stress, nutrition, and health issues.
Read Why
Instagram DM not opening issues can occur due to app problems or internet connection issues.
Read Why
Computer suddenly shutting down and restarting can occur due to hardware and software related issues.
Read Why
Giving a child a name from the Quran ensures religious connection and a meaningful, blessed choice.
Read WhyHealth problems often arise from daily habits or small unnoticed factors. This section explains simple but common topics such as why people get sick. It explores the body reactions and common health issues. This is not medical advice; consult a doctor.
Yes, the site is completely free to use. You dont need to register, and you can access all why questions. Our goal is to ensure that everyone can quickly and easily get the information they are curious about.
On the site, you can find answers to why questions in various fields such as science, health, technology, nature, culture, and daily life. Our goal is to explain the reasons behind various topics clearly and reliably.
You can quickly find your question using the search bar or category filters. Popular and recently added questions are also listed on the homepage, allowing you to save time and access information faster.
New why questions are added regularly. With weekly or monthly updates, users can access fresh content and learn up-to-date information on the topics they are curious about.
Yes, our answers rely on reliable sources as much as possible. Scientific studies, articles, or other trustworthy references are provided so that users can see the basis of the information.
The site is fully mobile-friendly. You can access all content easily using a smartphone or tablet, read questions, and view answers. Fast and smooth usage is ensured on mobile devices.
Our answers are prepared based on expert opinions, scientific research, and reliable sources. Providing accurate information is our priority, allowing users to confidently learn about the topics they are curious about.
Answers are prepared using references from experts and reliable sources, written in a clear and simple manner. Each answer is designed to explain the cause-and-effect relationship clearly.