Causes of Space Pollution?
Space pollution causes are briefly explained. The debris accumulated in orbit poses serious danger to Earth.
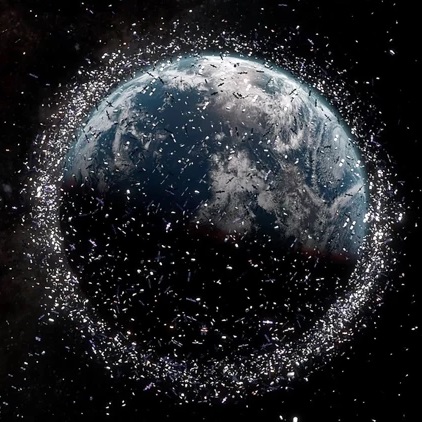

Why space pollution occurs and what its causes are in brief
Space pollution arises from many different reasons.1- Satellites that have reached the end of their service life remain in orbit even after completing their missions.
2- The upper stages of rockets drift uncontrollably after their fuel is exhausted.
3- Collisions between satellite and rocket parts create thousands of small fragments.
4- Missile and target parts used in old military tests also become permanent debris in orbit. These pieces move at speeds of up to 28,000 kilometers per hour, so even a small screw can cause major damage if it hits an active satellite.
According to NASA and ESA data, there are more than 30,000 debris pieces larger than 10 centimeters and millions smaller than 1 millimeter orbiting the Earth. This density has raised concerns that future satellite collisions could trigger a chain reaction.
The future impact of space pollution and solutions
The greatest danger of space pollution is the damage it can cause to active satellites orbiting the Earth. Since communication, weather forecasting, navigation, and military systems depend on these satellites, even a single collision can lead to large-scale data disruptions. Scientists therefore focus on orbital cleanup. New technologies aim to direct unused satellites back into the atmosphere for controlled burning. In addition, reusable rocket systems are being developed to ensure that every piece sent into space can be tracked. However, this process is possible not only through technology but also through international cooperation. Countries must develop joint orbital policies to prevent new debris generation and reduce existing waste.In short, the cause of space pollution is the release and abandonment of man-made waste into space after technological activities. While space exploration represents great progress for humanity, maintaining sustainability requires orbital order and environmental awareness. /