Why Does the Moon Constantly Change Shape?
The short answer to why the Moon constantly changes shape is that sunlight reaches it from different angles during its orbit around Earth.
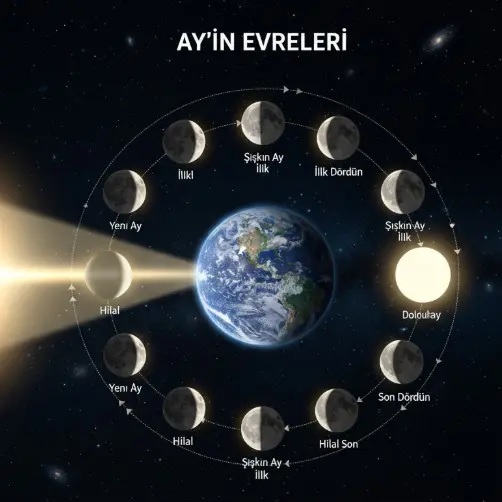
Why does the Moon constantly appear different
To understand why the Moon constantly takes on different shapes, one must examine the geometric relationship between the Moon, Earth, and the Sun. The Moon does not produce its own light; it only reflects the sunlight it receives. Since it completes one orbit around Earth in about twenty nine and a half days, the illuminated portion of its surface becomes visible from different angles throughout this period. Scientists summarize the basic principles explaining the Moon’s phases as follows.
1- As the Moon’s position changes, the visible illuminated portion of its surface also changes.
2- Sunlight always illuminates half of the Moon, but observers on Earth cannot always see the entire lit half.
3- The waxing and waning of the lunar phases result from the changing proportion of reflected light visible from Earth.
4- Phases such as new moon, first quarter, full moon, and last quarter occur naturally as the Moon progresses along its orbit.
This process is grounded in the linear propagation of light and the Moon’s orbital motion. While the Moon receives the same amount of light at all times, the part visible from Earth depends solely on its relative position. For this reason, the Moon may appear as a thin crescent, a half circle, or a full disk, and this change occurs entirely within a predictable physical framework.