Why do solar and lunar eclipses occur?
Solar and lunar eclipses occur when the Earth, Moon, and Sun align in specific positions, causing shadow events.
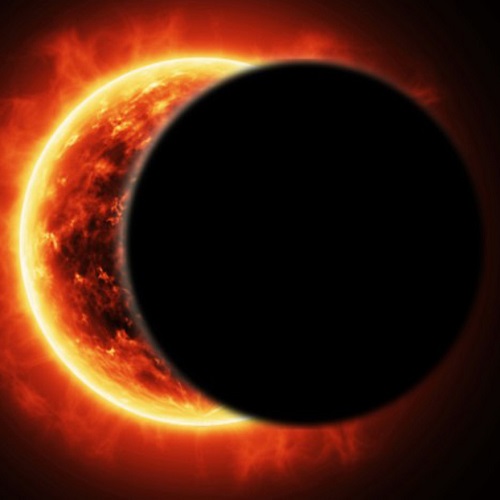

How solar and lunar eclipses happen
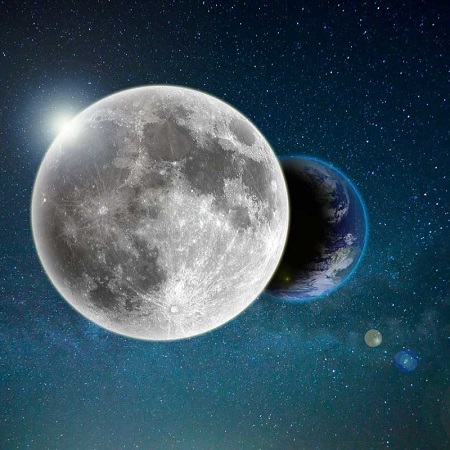
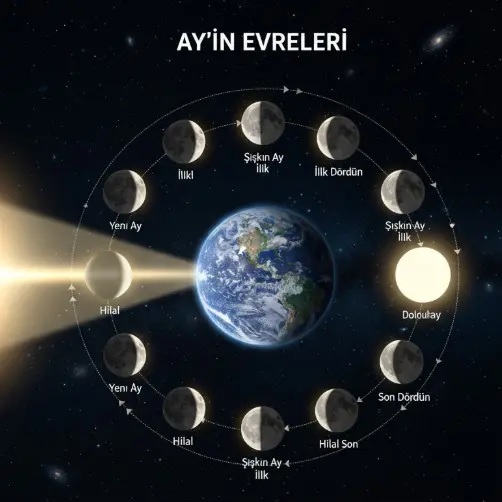
Eclipses occur due to the alignment of celestial bodies along a specific plane. The Moon orbits the Earth at a tilted angle, which is why eclipses do not happen every month. However, when the Moon passes through one of its orbital nodes and comes between the Earth and the Sun, a solar eclipse occurs. Conversely, when the Moon moves behind the Earth, a lunar eclipse happens. 1- Solar eclipses are usually short and visible only from specific regions. 2- Lunar eclipses, however, can be seen from anywhere on Earth where it is nighttime. During these events, factors such as the angle of shadows, the intensity of sunlight, and the amount of dust in the atmosphere affect the color and brightness of the eclipse.
The importance and effects of eclipses in nature
Eclipses hold deep significance both scientifically and culturally. Astronomers use them to study the orbits of the Sun and Moon, the way light refracts in the atmosphere, and to refine calculations related to space and time. The answer to why solar and lunar eclipses occur lies within the flawless order of celestial mechanics. Throughout human history, these events were often seen as supernatural, but scientific understanding has revealed them as perfect demonstrations of cosmic mathematics. Today, eclipses remain one of the most fascinating ways for scientists and sky enthusiasts alike to observe the harmony of the universe. /